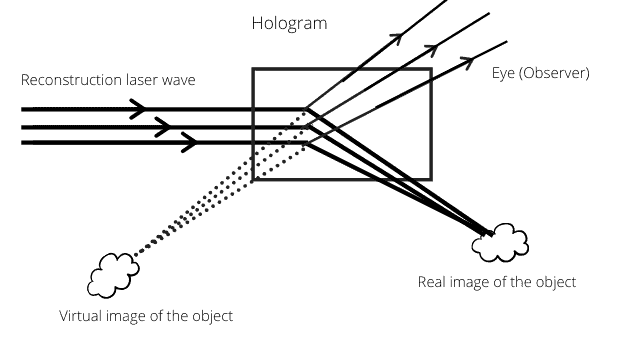
Holography is a technique for recording the interference pattern of light waves from an object and then reconstructing a three-dimensional image of the object from that pattern. Holograms are created by shining a laser beam onto an object and then splitting the beam into two beams. One beam is directed at the object, and the other beam is used as a reference beam. The object beam and the reference beam interfere with each other, creating an interference pattern on a piece of photographic film. When the film is developed, it contains a hologram that can be used to reconstruct the three-dimensional image of the object.
The word “holography” comes from the Greek words “holos” (whole) and “gramma” (message). Holograms are often described as three-dimensional photographs, but they are actually much more than that. Photographs only record the intensity of light waves, while holograms record both the intensity and the phase of light waves. This means that holograms can be used to reconstruct not only the shape of an object, but also its color, texture, and depth.
Holography was invented in 1947 by Dennis Gabor, a Hungarian physicist. Gabor was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1971 for his work on holography. The first practical holograms were created in the early 1960s by Emmett Leith and Juris Upatnieks, two American physicists.
Holography has a wide range of applications, including:
- 3D imaging: Holograms can be used to create realistic 3D images of objects. This technology is used in a variety of applications, including museum exhibits, medical imaging, and virtual reality.
- Security: Holograms can be used to create security features on documents, such as credit cards and passports. These features make it difficult to counterfeit these documents.
- Interferometry: Holograms can be used to measure the properties of objects, such as their shape, size, and surface texture. This technology is used in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, engineering, and medicine.
- Art: Holograms are used in a variety of art forms, including sculpture, painting, and photography. This technology allows artists to create new and innovative works of art.
Holography is a rapidly developing field with many potential applications. As the technology continues to improve, we can expect to see even more innovative and exciting uses for holograms in the future.
Here are some additional details about the different types of holograms:
- Transmission holograms: These holograms are created when the object beam and the reference beam are both transmitted through the photographic film. When the hologram is illuminated with a laser beam, the object beam is reconstructed and appears to be floating in front of the hologram. Transmission holograms are often used in museum exhibits and other educational applications.
- Reflection holograms: These holograms are created when the object beam is reflected off of the object and then interferes with the reference beam. When the hologram is illuminated with a laser beam, the object beam is reconstructed and appears to be behind the hologram. Reflection holograms are often used in security applications, such as credit cards and passports.
- Polarization holograms: These holograms are created when the object beam and the reference beam are polarized in different directions. When the hologram is illuminated with a laser beam, the object beam is reconstructed only if the viewer’s eyes are aligned with the polarization of the laser beam. Polarization holograms are often used in military and industrial applications.
Holography is a fascinating and versatile technology with many potential applications. As the technology continues to improve, we can expect to see even more innovative and exciting uses for holograms in the future.